We found 376 results that contain "it"
Posted on: #iteachmsu

Data structures
A data structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and storing data. There are several basic and advanced types of data structures, all designed to arrange data to suit a specific purpose. Data structures make it easy for users to access and work with the data they need in appropriate ways. Most importantly, data structures frame the organization of information so that machines and humans can better understand it.
In computer science and computer programming, a data structure may be selected or designed to store data for the purpose of using it with various algorithms. In some cases, the algorithm's basic operations are tightly coupled to the data structure's design. Each data structure contains information about the data values, relationships between the data and -- in some cases -- functions that can be applied to the data.
For instance, in an object-oriented programming language, the data structure and its associated methods are bound together as part of a class definition. In non-object-oriented languages, there may be functions defined to work with the data structure, but they are not technically part of the data structure.
Why are data structures important?
Typical base data types, such as integers or floating-point values, that are available in most computer programming languages are generally insufficient to capture the logical intent for data processing and use. Yet applications that ingest, manipulate and produce information must understand how data should be organized to simplify processing. Data structures bring together the data elements in a logical way and facilitate the effective use, persistence and sharing of data. They provide a formal model that describes the way the data elements are organized.
Data structures are the building blocks for more sophisticated applications. They are designed by composing data elements into a logical unit representing an abstract data type that has relevance to the algorithm or application. An example of an abstract data type is a "customer name" that is composed of the character strings for "first name," "middle name" and "last name."
It is not only important to use data structures, but it is also important to choose the proper data structure for each task. Choosing an ill-suited data structure could result in slow runtimes or unresponsive code. Five factors to consider when picking a data structure include the following:
What kind of information will be stored?
How will that information be used?
Where should data persist, or be kept, after it is created?
What is the best way to organize the data?
What aspects of memory and storage reservation management should be considered?
How are data structures used?
In general, data structures are used to implement the physical forms of abstract data types. Data structures are a crucial part of designing efficient software. They also play a critical role in algorithm design and how those algorithms are used within computer programs.
Early programming languages -- such as Fortran, C and C++ -- enabled programmers to define their own data structures. Today, many programming languages include an extensive collection of built-in data structures to organize code and information. For example, Python lists and dictionaries, and JavaScript arrays and objects are common coding structures used for storing and retrieving information.
Software engineers use algorithms that are tightly coupled with the data structures -- such as lists, queues and mappings from one set of values to another. This approach can be fused in a variety of applications, including managing collections of records in a relational database and creating an index of those records using a data structure called a binary tree.
In computer science and computer programming, a data structure may be selected or designed to store data for the purpose of using it with various algorithms. In some cases, the algorithm's basic operations are tightly coupled to the data structure's design. Each data structure contains information about the data values, relationships between the data and -- in some cases -- functions that can be applied to the data.
For instance, in an object-oriented programming language, the data structure and its associated methods are bound together as part of a class definition. In non-object-oriented languages, there may be functions defined to work with the data structure, but they are not technically part of the data structure.
Why are data structures important?
Typical base data types, such as integers or floating-point values, that are available in most computer programming languages are generally insufficient to capture the logical intent for data processing and use. Yet applications that ingest, manipulate and produce information must understand how data should be organized to simplify processing. Data structures bring together the data elements in a logical way and facilitate the effective use, persistence and sharing of data. They provide a formal model that describes the way the data elements are organized.
Data structures are the building blocks for more sophisticated applications. They are designed by composing data elements into a logical unit representing an abstract data type that has relevance to the algorithm or application. An example of an abstract data type is a "customer name" that is composed of the character strings for "first name," "middle name" and "last name."
It is not only important to use data structures, but it is also important to choose the proper data structure for each task. Choosing an ill-suited data structure could result in slow runtimes or unresponsive code. Five factors to consider when picking a data structure include the following:
What kind of information will be stored?
How will that information be used?
Where should data persist, or be kept, after it is created?
What is the best way to organize the data?
What aspects of memory and storage reservation management should be considered?
How are data structures used?
In general, data structures are used to implement the physical forms of abstract data types. Data structures are a crucial part of designing efficient software. They also play a critical role in algorithm design and how those algorithms are used within computer programs.
Early programming languages -- such as Fortran, C and C++ -- enabled programmers to define their own data structures. Today, many programming languages include an extensive collection of built-in data structures to organize code and information. For example, Python lists and dictionaries, and JavaScript arrays and objects are common coding structures used for storing and retrieving information.
Software engineers use algorithms that are tightly coupled with the data structures -- such as lists, queues and mappings from one set of values to another. This approach can be fused in a variety of applications, including managing collections of records in a relational database and creating an index of those records using a data structure called a binary tree.
Posted by:
Sharon

Posted on: #iteachmsu


Data structures
A data structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing...
Posted by:
Wednesday, Jul 21, 2021
Posted on: #iteachmsu

ASSESSING LEARNING
What Is Robotics?
Robotics is the intersection of science, engineering, and technology that produces machines, called robots, that substitute for (or replicate) human actions. Pop culture has always been fascinated with robots. R2-D2. Optimus Prime. WALL-E. These over-exaggerated, humanoid concepts of robots usually seem like a caricature of the real thing...or are they more forward-thinking than we realize? Robots are gaining intellectual and mechanical capabilities that don’t put the possibility of an R2-D2-like machine out of reach in the future.As technology progresses, so too does the scope of what is considered robotics. In 2005, 90% of all robots could be found assembling cars in automotive factories. These robots consist mainly of mechanical arms tasked with welding or screwing on certain parts of a car.
Posted by:
Chathuri Super admin..

Posted on: #iteachmsu


What Is Robotics?
Robotics is the intersection of science, engineering, and technolog...
Posted by:
ASSESSING LEARNING
Wednesday, Apr 28, 2021
Posted on: #iteachmsu

Alexa Development
Skills are like apps for Alexa, and provide a new channel for your content and services. Skills let customers use their voices to perform everyday tasks like checking the news, listening to music, playing a game, and more. Organizations and individuals can publish skills in the Alexa Skills Store to reach and delight customers on hundreds of millions of Alexa devices.
Authored by:
Divya Sawant

Posted on: #iteachmsu


Alexa Development
Skills are like apps for Alexa, and provide a new channel for your ...
Authored by:
Friday, Dec 4, 2020
Posted on: #iteachmsu

PDF : widespread seabird and marine mammal mortality
widespread seabird and marine mammal mortality
Many scientists see recent climate-related mass die-offs, including the coral bleaching of the Great Barrier Reef and widespread seabird and marine mammal mortality in the Northeastern Pacific linked to a marine heat wave, as warning signs of impending biodiversity collapse, said lead author Alex Pigot, a biodiversity researcher at University College, London. The new study shows that nowhere on Earth will escape the impacts.
Many scientists see recent climate-related mass die-offs, including the coral bleaching of the Great Barrier Reef and widespread seabird and marine mammal mortality in the Northeastern Pacific linked to a marine heat wave, as warning signs of impending biodiversity collapse, said lead author Alex Pigot, a biodiversity researcher at University College, London. The new study shows that nowhere on Earth will escape the impacts.
Authored by:
Chathuri hewapathirana

Posted on: #iteachmsu


PDF : widespread seabird and marine mammal mortality
widespread seabird and marine mammal mortality
Many sci...
Many sci...
Authored by:
Friday, Apr 10, 2020
Posted on: #iteachmsu

DISCIPLINARY CONTENT
Help and Support Resources
Customer Support Process
MSU IT is available 24/7 to support your IT needs. Contact the MSU IT Service Desk using one of the methods listed below:
Option 1:Call (517) 432-6200 or toll-free at (844) 678-6200
Always call if you need a prompt response
You will be presented with six options, for most problems in your area you will want to dial six for general IT Service Desk assistance. The other options are as follows:
Option 1: Classroom Support
Option 2: Distance Learning Services such as D2L
Option 3: Clinical and Radiology Systems such as EMR, ARIS, or PACS
Option 4: EBS or other business or administrative services
Option 5: Student assistance with Internet access, login, or email questions
Option 6: Wait on the line (general IT Service Desk assistance
Choose Option 6 or stay on the line for assistance with anything not specifically listed above.
Option2: Email ithelp@msu.edu<mailto:ithelp@msu.edu>
Option 3: Use the Self-Service Portal <https://uss.itservicedesk.msu.edu/web/frontoffice/login?redirect=/>
Log in with your NetID
Select either "Report an Issue," "Request a Service," or "Search Knowledge Base" depending on your needs
Contact ithelp@msu.edu<mailto:ithelp@msu.edu> if pre-populated fields are not correct
If using Internet Explorer, consult Knowledge Base document #404713 if errors are encountered
Help Resources
Perform the following steps to gain access to tutorials, help documentation, post questions, and see release notes:
Login to #iteachmsu Commons
Navigate to the Help and Support Group from the Home screen.
Click on the Join Group button
Check the "Getting started in the #iteachmsu Digital Commons" playlist for tutorials and helpdesk information.
MSU IT is available 24/7 to support your IT needs. Contact the MSU IT Service Desk using one of the methods listed below:
Option 1:Call (517) 432-6200 or toll-free at (844) 678-6200
Always call if you need a prompt response
You will be presented with six options, for most problems in your area you will want to dial six for general IT Service Desk assistance. The other options are as follows:
Option 1: Classroom Support
Option 2: Distance Learning Services such as D2L
Option 3: Clinical and Radiology Systems such as EMR, ARIS, or PACS
Option 4: EBS or other business or administrative services
Option 5: Student assistance with Internet access, login, or email questions
Option 6: Wait on the line (general IT Service Desk assistance
Choose Option 6 or stay on the line for assistance with anything not specifically listed above.
Option2: Email ithelp@msu.edu<mailto:ithelp@msu.edu>
Option 3: Use the Self-Service Portal <https://uss.itservicedesk.msu.edu/web/frontoffice/login?redirect=/>
Log in with your NetID
Select either "Report an Issue," "Request a Service," or "Search Knowledge Base" depending on your needs
Contact ithelp@msu.edu<mailto:ithelp@msu.edu> if pre-populated fields are not correct
If using Internet Explorer, consult Knowledge Base document #404713 if errors are encountered
Help Resources
Perform the following steps to gain access to tutorials, help documentation, post questions, and see release notes:
Login to #iteachmsu Commons
Navigate to the Help and Support Group from the Home screen.
Click on the Join Group button
Check the "Getting started in the #iteachmsu Digital Commons" playlist for tutorials and helpdesk information.
Authored by:
Rashad Muhammad
Posted on: #iteachmsu

Help and Support Resources
Customer Support Process
MSU IT is available 24/7 to support your I...
MSU IT is available 24/7 to support your I...
Authored by:
DISCIPLINARY CONTENT
Thursday, Sep 28, 2023
Posted on: #iteachmsu

NAVIGATING CONTEXT
TESt USer Aricle : 01
Launched in April 2006 as a statistical machine translation service, it used United Nations and European Parliament documents and transcripts to gather linguistic data. Rather than translating languages directly, it first translates text to English and then pivots to the target language in most of the language combinations it posits in its grid,[4], with a few exceptions including Catalan-Spanish.[5] During a translation, it looks for patterns in millions of documents to help decide on which words to choose and how to arrange them in the target language. Its accuracy, which has been criticized and ridiculed on several occasions,[6] has been measured to vary greatly across languages.[7] In November 2016, Google announced that Google Translate would switch to a neural machine translation engine - Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT) - which translates "whole sentences at a time, rather than just piece by piece. It uses this broader context to help it figure out the most relevant translation, which it then rearranges and adjusts to be more like a human speaking with proper grammar".[8] Originally only enabled for a few languages in 2016, GNMT is used in all 109 languages in the Google Translate roster as of 2020, except for Kyrgyz, Latin, and the Belarusian, Maltese and Sundanese to other languages pairs.[9]
Authored by:
Chathuri

Posted on: #iteachmsu


TESt USer Aricle : 01
Launched in April 2006 as a statistical machine translation&nb...
Authored by:
NAVIGATING CONTEXT
Thursday, Apr 9, 2020
Posted on: #iteachmsu
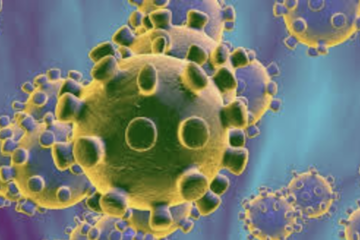
DISCIPLINARY CONTENT
virology Artilce
Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are ubiquitous, well adapted to their host and cleverly sequestered away from immune responses. HPV infections can be productive, subclinical or latent in both skin and mucosa. The causal association of HPV with cervical cancer, and increasingly with rising numbers of squamous cell carcinomas at other sites in both men and women, is increasingly recognised, while the morbidity of cutaneous HPV lesions, particularly in the immunosuppressed population is also significant. This chapter sets out the range of infections and clinical manifestations of the consequences of infection and its persistence and describes why HPVs are both highly effective pathogens and carcinogens, challenging to eliminate.
Authored by:
Chathuri hewapathirana

Posted on: #iteachmsu


virology Artilce
Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are ubiquitous, well adapted to ...
Authored by:
DISCIPLINARY CONTENT
Monday, Mar 23, 2020
Posted on: #iteachmsu

ASSESSING LEARNING
Hydrosphere
Hydrosphere, discontinuous layer of water at or near Earth’s surface. It includes all liquid and frozen surface waters, groundwater held in soil and rock, and atmospheric water vapour.Water is the most abundant substance at the surface of Earth. About 1.4 billion cubic km (326 million cubic miles) of water in liquid and frozen form make up the oceans, lakes, streams, glaciers, and groundwaters found there. It is this enormous volume of water, in its various manifestations, that forms the discontinuous layer, enclosing much of the terrestrial surface, known as the hydrosphere.
Posted by:
Chathuri Super admin..

Posted on: #iteachmsu


Hydrosphere
Hydrosphere, discontinuous layer of water at or near Eart...
Posted by:
ASSESSING LEARNING
Friday, Apr 23, 2021



